Ocean Wave Styles and Patterns
Ocean Wave Styles and Patterns
OCEANIC WAVES
CHARACTERISTICS OF WAVE MOTION
WIND WAVES, SEA, AND SWELL
WAVES IN SHALLOW WATER
TSUNAMIS
STANDING WAVES
INTERNAL WAVES

Wind energy is transferred to surface waters by frictional processes to generate surface ocean currents and waves.
OCEANIC WAVES
Oceanic waves may be approximated mathematically by a sine wave, and therefore exhibit a smooth, regular oscillation.
Wave Height
( H )
vertical distance between
any crest and succeeding trough
Wavelength
( L )
horizontal distance between
successive crests or troughs
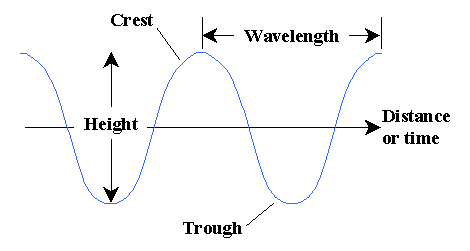
Wave Period
( T )
time interval between
the passage of successive crests
Celerity (Wave Speed)
( C )
C = L / T
(or wavelength / period)
Wave oscillation is also described by frequency,
1/T (the number of waves passing a stationary point in a given length of time)
CHARACTERISTICS OF WAVE MOTION:
- waves impart vertical, circular orbits to individual parcels of
water without any substantial net horizontal movement
- orbital diameter of water parcels at the surface approximately equals the wave height
- vertical motion becomes negligible at depths greater than about one-half the wavelength (i.e., L/2)
- motion in water depths exceeding L/2 (and therefore unaffected by the ocean bottom) will produce deep water waves
- circular orbits of water parcels become flattened as a result of bottom interference and form shallow water waves
and is controlled by the depth of water!! The speed of deep water waves is independent of the depth
and is determined by wavelength and period!!
Deep water waves are therefore dispersive (i.e., wave speed is frequency dependent) and
wave separation will occur according to celerity, length, and period in the 'open' ocean!!
Any complicated ocean wave surface can therefore be constructed (theoretically)
by a combination of simple sine waves of different height, period, and phase!!
- interaction of multiple wave forms results in wave interference (i.e., the merging and/or separation of numerous waves)
- constructive wave interference results from the coincidence of several wave crests or troughs
- coincidence of individual crests and troughs results in destructive wave interference
WIND WAVES, SEA, AND SWELL:
- growth of wind-generated surface waves is controlled by the velocity of the wind, wind duration, and fetch
- the height of surface waves increases with increasing wind speed and with increasing duration and fetch of the wind
- together with height, the dominant wavelength also increases
- surface tension or capillary waves (L < 2 cm) are the direct products of the wind stress exerted on the sea surface
- tend to 'feed' wind energy into larger gravity waves (waves of characteristically longer wavelengths)

Capillary waves formed on the surface of the ocean. Waves eventually attain a maximum significant height, or fully developed seas!!
Maximum wave height is determined by the point at which the energy imparted to the waves
by the wind is equal to the energy lost by the waves through breaking or other frictional loss!!

Whitecap formation typical of fully developed seas.

Formation of open ocean swells
- considerable wave energy is lost through white capping
- theoretical limit of wave stability approximated by a wave height to wavelength ratio of 1/7
- if the ratio is exceeded, the wave crest will be driven forward by the wind more rapidly than the wave itself
- after the wind has abated or shifted (or the waves have migrated away from the dominant wind field) the energy will continue to propagate as swell (characteristically smooth, long-crested, longer period waves)
- lose energy only gradually, via internal friction and air resistance and by energy dissipation through 'fanning out'
Most wind-generated waves eventually reach shorelines and dissipate any remaining energy.

WAVES IN SHALLOW WATER:
- shoreline contact results in shallow water wave transformations, wave refraction, and collapse as shore breakers
- wave induced motion is most greatly affected by the presence of ocean bottom where the depth is less than L/20
- speed of wave propagation and wavelength decrease, but the wave
period remains unchanged
- wave height eventually exceeds wavelength
- results in the eventual collapse of the wave and formation of breakers
- direction of wave approach also changes as waves enter shallow water
- known as wave refraction
- wave crests rotate to become parallel to the bottom depth contours (i.e., refract toward shallow water)
- results from the variable celerity of different parts of the same wave crest traveling shoreward
TSUNAMIS:
- large waves caused by the sudden displacement of ocean water (often resulting from earthquakes or volcanic eruptions)
- characterized by very long periods and therefore behave like shallow
water waves
- deep water wave formation occurs in water depths greater than L/2
- tsunami wavelengths typically exceed 100 km (L/2 = 50 km) and the ocean rarely exceeds 11 km depth
- imperceptible in the open ocean (typically less than one meter in height)
- tsunami speed (often more than 800 kph) is drastically reduced on the continental shelf, and height increases dramatically

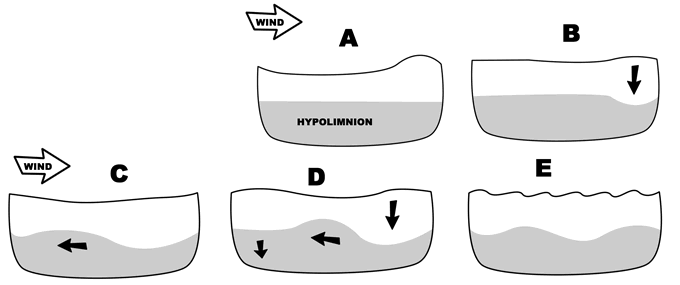
STANDING WAVES:
- oscillate vertically about a fixed point (or node) with no progressive movement (e.g., seiches)
- typically form in response to the 'rocking' of a water mass within a
confined space
- commonly form in large lakes as a response to intense storm activity
- winds 'pile' water at the downwind of the lake, and when the wind stress is removed, the water returns 'downslope'
- can also be generated in partially enclosed basins, such as bays, harbors, and estuaries
INTERNAL WAVES:
- energy travels along internal 'surfaces' (e.g., density discontinuities or pycnoclines) as wave pulses
- subsurface manifestations is simply a regular rising and sinking of water layers, identified as internal waves
- travel at much slower speeds than surface waves, but characteristically exhibit large periods and wavelengths
- have wave heights on the order of several meters, but larger internal waves can attain heights in excess of 100 meters
- cause of internal waves is poorly understood - may be attributed to tidal forces or wind and pressure fluctuations


