Flywheel Energy Storage
Flywheel Energy Storage
FESS Flywheel Energy Storage Systems Basics
Two main Categories of Flywheels
How Flywheels Store and Release Electrical Energy
Benefits of Flywheel Energy Storage
Drawbacks of Flywheel Energy Storage
Practical Uses of Flywheel Storage
Flywheels Versus Other Storage Systems
Sources
FESS Flywheel Energy Storage Systems Basics
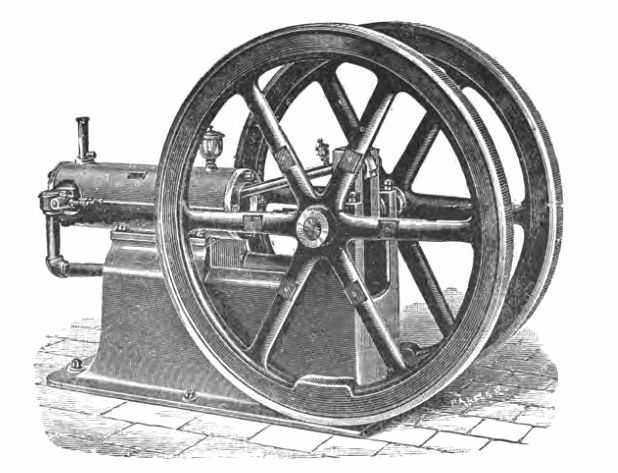
Flywheels have been in use for a long time
In Australia do flywheels have a role as energy storage devices?
All flywheel energy systems use the same basic concepts to store energy.
- A rotating mass, ideally spinning in a vacuum. .
- As frictionless a rotation point as possible,
- Power is stored by rotating the mass of the flywheel;
- Power is generated by the inertia of slowing down that same flywheel
Two Main Categories of Flywheels
Flywheel energy storage systems can be divided into two main categories based on the speed of the rotor:
- High-speed flywheels- made from composite materials like carbon fiber and fiberglas, typically operate at speeds between 20,000 and 60,000 revolutions per minute (RPM) and can store energy for a few seconds to a few minutes. They are commonly used for short-term energy storage applications such as providing backup power to critical loads, stabilizing grid frequency, and smoothing out fluctuations in renewable energy sources such as wind and solar.
- Low-speed flywheels - usually made from steel - operate at speeds between 1,000 and 10,000 RPM and can store energy for several hours. Low-speed flywheel energy storage systems, are better suited for longer-term energy storage applications such as off-grid power systems, remote locations, and microgrids.
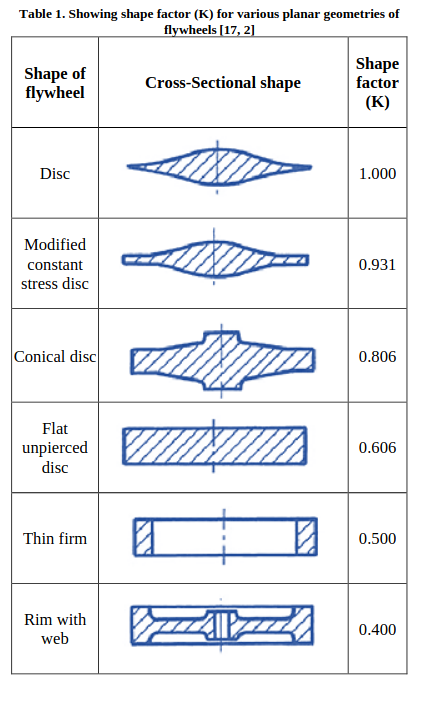
Flywheels have different cross-sectional shapes depending on their use.
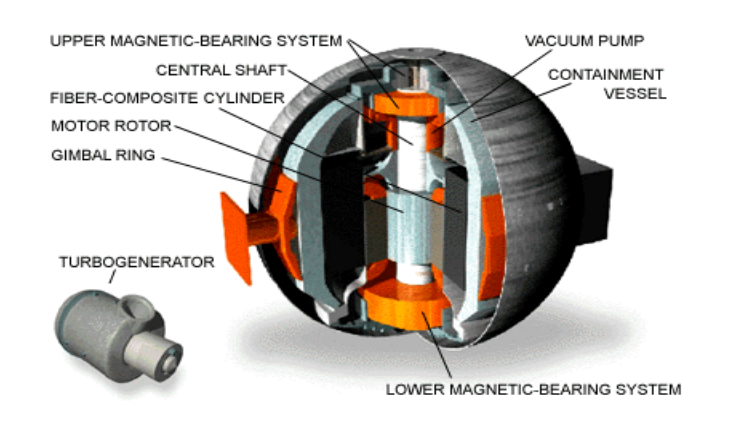
How Flywheels Store and Release Electrical Energy
In a flywheel energy storage system, the rotor is connected to a motor/generator.
This motor/generator can either accelerate the rotor to store energy or decelerate the rotor to convert the stored energy into electrical power.
When electrical energy is supplied to the motor, it spins the rotor faster, which stores energy in the form of rotational kinetic energy. The energy is stored by increasing the speed of the rotor, and the amount of energy stored is proportional to the square of the rotational speed and the moment of inertia of the rotor.
The rotational kinetic energy stored in the flywheel can be calculated using the formula:
Ek = ½ Iω2
- Ek is the rotational kinetic energy - that is the enerft stored
- I is the moment of inertia, which depends on the flywheel’s mass and how that mass is spread out relative to the axis of rotation.
- ω is the angular velocity, or how fast the flywheel is spinning.
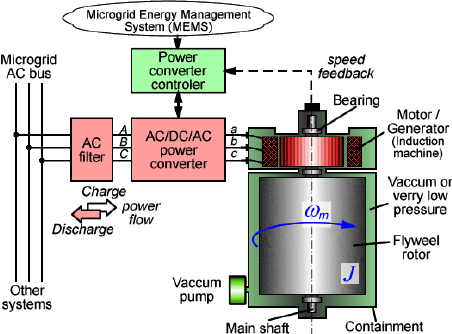
Typical High Speed Flywheel
The rotor is designed to be as light as possible while still having a high moment of inertia to maximize the amount of energy that can be stored. The rotor is also housed in a vacuum chamber to reduce air resistance and minimize energy loss due to friction.
The rotor is suspended in the vacuum chamber by magnetic bearings, which are used to levitate the rotor and reduce friction. The magnetic bearings also allow the rotor to spin at high speeds without touching any solid surfaces, which helps minimize wear and tear and increases the efficiency of the system.
When energy is needed, the stored kinetic energy in the spinning rotor is converted back into electrical energy through the generator. The generator is connected to an electrical load, such as a motor or a grid, and as the rotor slows down, the rotational energy is converted back into electrical energy. The electrical energy can then be used to power devices or fed into the grid as needed.
The rate at which energy can be stored or discharged from a flywheel energy storage system depends on the design of the system, including the mass and shape of the rotor, the speed at which it spins, and the efficiency of the motor and generator.
Additionally, the energy storage capacity of a flywheel energy storage system is limited by the maximum rotational speed of the rotor and the maximum allowable stresses on the rotor materials.
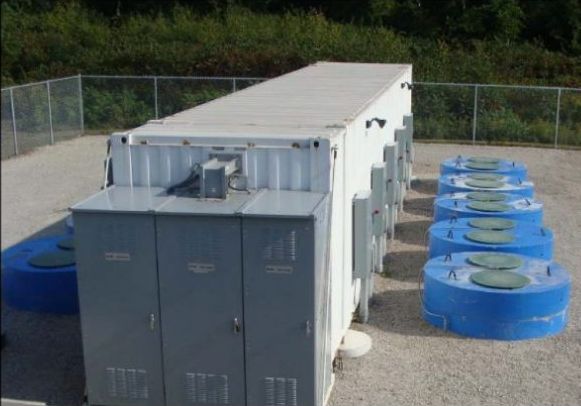

A commercial flywheel storage facility
Benefits of Flywheel Energy Storage
- High Power Density: Flywheel energy storage systems can store a large amount of energy in a small space, making them suitable for applications where space is limited.
- Fast Response Time: Flywheel energy storage systems can respond quickly to changes in demand or supply. This makes them useful for grid stabilization and renewable energy integration.
- High Efficiency: Flywheel energy storage systems can convert energy back and forth with very little loss, making them cost-effective in the long run.
- Long Cycle Life: Flywheel energy storage systems can last for many years without significant degradation, making them a reliable and low-maintenance energy storage solution.
- Low Maintenance: Flywheel energy storage systems are robusr, durable, long-lived and as a result need a lot less human intervention to keep them in working order
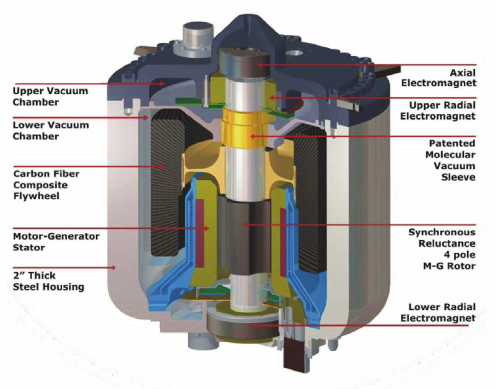
example of commercial flywheel design
Drawbacks of Flywheel Energy Storage
- High Cost: Flywheel energy storage systems require expensive, though easy to obtain, high-quality materials needed to construct the rotor, vacuum chamber, and magnetic bearings.
- Limited Energy Storage Capacity: Flywheel energy storage systems have limited energy storage capacity, and they are best suited for short-term energy storage applications.
- Risk of Mechanical Failure: The high rotational speeds of the flywheel rotor mean that there is a risk of mechanical failure if the rotor is not properly contained. A catastrophic failure could lead to significant damage and safety risks. this also means they must be kept in housings that will keep any broken bits from flying off and doing damage
- Energy Loss due to Friction: Despite the use of magnetic bearings, some energy is lost due to friction, which reduces the efficiency of the system. But they have better energy efficiency than most storage systems.
- Sensitivity to Temperature: It is difficult to dissipate heat when a flywheel is working in a vacuum. Flywheels must be designed to operate within a specific temperature range to prevent thermal expansion or contraction, which could lead to mechanical failure.
Practical Uses of Flywheel Storage
Flywheel energy storage is suitable for:
- high-power,
- fast-response, and
- high-frequency scenarios
- UPS Uninterrupted Power Supply - Emergency back-up power -
Global data centers, communication base stations, and important
activities all have clear requirements for UPS Uninterrupted Power
Supply. At present, the combination mode of chemical battery + diesel
generator is mainly used. Compared with the current chemical battery
such as UPS lithium battery, the flywheel energy storage has the
advantages of faster response, large instantaneous power, small
footprint and long service life.
Example: UPS Uninterrupted Power Supplies home computer - when there is a power outage a flywheel "battery" can immediately regain power, result in less stress on electrical batteries resulting in longer life and overall prolonged UPS life. However the flywheel will only supply power to overcome the shock load on startup, afterwards the chemical batteries will take up the load.
small UPS flywheel battery can immediately come on line in a power blackout - Frequency Power Modulation for Renewable Energy: - Power
input to a system by wind and solar can be quite variable for example
on a day with scattered clouds and gusty winds. By using about 2%
flywheel energy storage it is possible to smooth out these power
fluctuations. Flywheel frequency modulation is able respond quicker
than than the electrochemical frequency modulation at power stations.
It can quickly and effectively stabilize fluctuating loads, buffer power generation output transients, and support power grid frequency and voltage.
- Hybrid Energy Storage Systems: Flywheel energy storage could be combined with other energy storage technologies such as batteries or pumped hydro to create hybrid energy storage systems. Hybrid systems could provide the benefits of both technologies, extending the useful length of time they can provide electricity.
- Transportation Applications: Storing energy from regenerative braking. At present, the electric energy recovered by subway trains entering the station is consumed by means of resistance heat dissipation, which has the problem of waste of resources and impact on the power grid. Flywheel energy storage will recover electric energy when the train enters the station, and release the electric energy when the train leaves the station and playing the role of energy saving and save 20% of electricity. For electric car fast charging stations, flywheels could reduce the instantaneous high demand on the power grid by providing a fast charge pile system.
- Space Applications: a simple weight on a long tether, spun up by a motor/generator using solar panel electricicty can provide electrical power while a satellite or space station is on the dark side of its earth orbit.
- Heavy Lifting in Industry - a much smaller diesel plant would be required for short heavy lifts (like opening a tilt bridge or canal lock) if potential energy was gradually stored in a heavy flywheel prior to the lift
Flywheels Versus Other Storage Systems
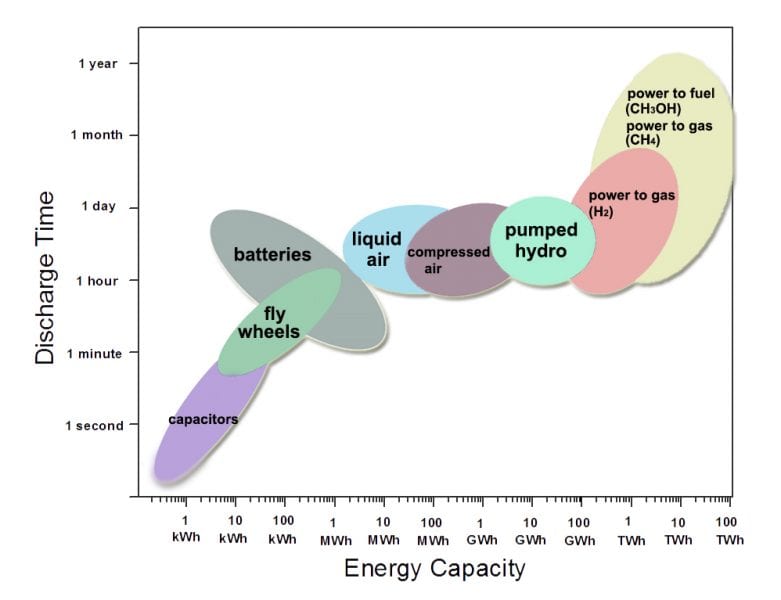
From the graph you can see that while (super) capacitors are great for getting things started for up to about a minute
So capacitors are good for starting a motor or initiating a system
Flywheels work well from a just under a minute up to around an hour.
So flywheels are best for smoothing sudden variations in a system.
In fact, for modest power requirements over relatively short duration, they can effectively substitute for chemical batteries
They have the added advantage of greater durability and longer lifespan.
They are also suited to work with batteries in a hybrid system and in doing so putting less strain on the batteries and extending their useful life.
In Australia do flywheels have a role as energy storage devices?
The answer is yes.
In our renewable energy mix with flywheels contributing just 2% would effectively regulate the ups and downs of a primarily solar and wind based power grid. This is a simple and fundamental practical use.
The increased use of public transport in a society determined to reduce the carbon footprint offers an ideal use for flywheels. On metro trains and electric buses, flywheels energised on entry to a stop from regenerative braking can provide electricity to assist in the acceleration on exit from a stop. a reduction in carbon footprint of about 20%.
When a UPS system starts up there is a heavy load on the batteries, the use of a flywheel to absorb this initial load for even small office / desktop computer/ data systems. These devices are now being marketed.
In large data centres flywheels will supply instant back up and power regulation negating the need to go nuclear.
We should act to include flywheels in our energy mix.
Future ideas - electric aircraft we could "launch by wire", a bit like an aircraft carrier using flywheel energy for take-off thus getting the aircraft in the air with full batteries and extending its flying time. Take-off could be either by mechanical means or by supplying flywheel electricity to the planes electric engines.
Sources
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Comparison-of-discharge-time-vs-capacity-of-energy-storage-technologies-24_fig2_306523823
https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/climate-busters/
https://www.windpowerengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/Vycom-flywheels.jpg
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Flywheel-energy-storage-system-structure_fig2_276026997
https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/analysis/has-flywheel-power-finally-come-of-age/
https://www.takomabattery.com/flywheel-energy-storage/
https://ziang.binghamton.edu/flywheel-technology/
https://greenenergymaterial.com/flywheel-energy-storage-in-21st-century/
https://ijettjournal.org/Volume-72/Issue-4/IJETT-V72I4P122.pdf
https://www.planete-energies.com/en/media/article/flywheel-energy-storage
https://www.omnicalculator.com/physics/flywheel-energy-storage
https://electricalengineerpro.com/flywheel-energy-storage-explained/
https://electricalengineerpro.com/energy-storage-system-explained/
https://www.ctc-n.org/technologies/flywheels

