

Fossil Fuels
adapted to HTML from lecture notes of Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane
University
Average Consumption
- The energy consumption of a nation is proportional to its Gross
National Product (GNP). (The higher the GNP of a nation, the higher
its consumption.)
- The minimun energy needed by an individual is 2000 calories per day.
- In a technological society, the average individual uses 230,000
calories per day.
| Calories per day |
Purpose |
| 10,000 |
Preparing food |
| 66,000 |
Home and Commerce |
| 91,000 |
Industry and Agriculture |
| 63,000 |
Transportation |
- We will essentially use up all the world's petroleum resources by
2050.
- We will essentially use up all the world's coal resources by 2500.



- The graph above illustrates the energy sources of mankind through
history. We are currently using more energy than ever before, due to
the availability of fossil fuels. Before 1500 A.D. we used slaves,
animals and firewood. When we run out of fossil fuels will we use
these sources again or find new technology?
Oil (U.S.A as an example)
- Oil compromises 40% of the total U.S. energy use.
- 400 billion barrels have been consumed in the world, to date.
- U.S. has a total resource of about 200 billion barrels. (Before
1950, we were the major producer of oil in the world.)
- There are 80 billion barrels of Oil resources remaining in the U.S.
- U.S. has not been self sufficient since 1950's, as at that point, it
became cheaper to import oil rather than to mine our remaining
resources.
- We use about 25% of world's oil, or about 6 billion barrels per
year.
- Alaska's North Slope contained about 10 billion barrels.
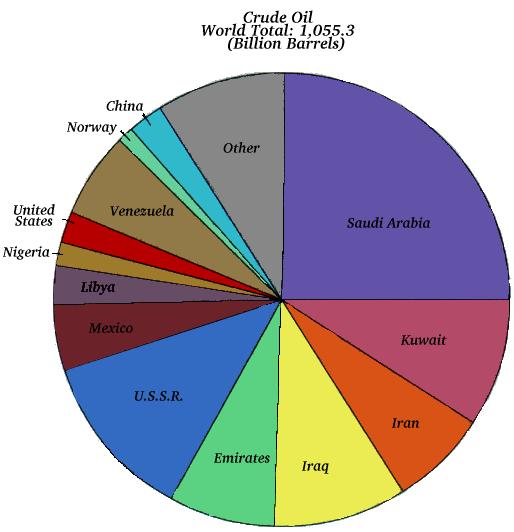
Most oil reserves are in a few large fields.

NOTE: for price per Litre divide by 3.785
| High Priced Locations (over $3 per gallon) |
| Location |
Average Pump price / gallon |
| Tokyo |
4.58 |
| Hong Kong |
3.87 |
| Paris |
3.58 |
| Milan, Italy |
3.54 |
| Amsterdam, Netherlands |
3.43 |
| Munich, Germany |
3.37 |
| Brussels, Belgium |
3.14 |
| Low Priced Locations (under $1.50 per gallon) |
| Location |
Average Pump price / gallon |
| Caracas, Venezuela |
0.21 |
| Riyadh, Saudi Arabia |
0.33 |
| Quito, Ecuador |
0.74 |
| Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates |
0.83 |
| United States |
1.11 |
| Bangkok, Thailand |
1.23 |
| Mexico City, Mexico |
1.44 |
| Nairobi, Kenya |
1.49 |
- Some countries have high gasoline prices due to taxes that are
levied to discourage use.
Formation of Oil
- Most Oil formed in marine environments.
- Organic rich sediments are deposited fast and buried before
decomposition. These sediments are mainly younger than 500 Million
Years.
- Organic material converted to oil and natural gas (hydrocarbons,
e.g.. Ch4) upon burial, by geothermal heat (150- 200 'F).
- Oil and gas migrate from source rock to permeable rock.
- If trapped oil and gas can be recovered.


Other Fossil Fuel Sources
Natural Gas
- Accounts for 25% of the U.S. energy use.
- U.S. has reserves of about 200 trillion cubic feet (TCF) .
- U.S. uses 20 TCF per year.
- the U.S. have reserves for a few decades only but it is still a
larger resource than oil.
- large Australian reserves on the Northwest Shelf
Oil Shale
- Essentially immature source rock. (Never got hot enough to release
the oil.)
- In the U.S., it is located in the Green River Formation, which is
spread out over Idaho, Utah and Colorado, and contains about 2
trillion barrels of oil.
- World wide reserves of oil only account for 0.7 trillion barrels
Tar Sand
- Major resource in Alberta, Canada. , Julia Creek, Australia
- Semiliquid- semisolid to solid petroleum in rock.
- Tar sands are relatively expensive to mine and have large
environmental impacts.








