Pollutants
Pollutants
back to Contents of Entire Course...
Persistant Pollutants
Water Pollution and How it Occurs
Flow of Pollutants
Selected Water Pollutants
adapted to HTML from lecture notes of Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane
University image from: http://compoundchem.com with thanks

Persistant Pollutants
Accumulates in our bodies over long periods of time. The US EPA, has set maximum standards, or limits, for many of these.
Lead -- Less than .05 ppm in water.
Arsenic -- Less than .05 ppm in water.
Mercury -- Less than .002 ppm in water.
Nitrates -- Less than 10 ppm in water.
Main sources are fertilizers and sewage.
Inhibits blood ability to carry oxygen.
Can not boil water to remove, like you can with bacteria and virii -- boiling only concentrates nitrates, making them more toxic. Epidimiology - Study of disease rates and what causes them. Often provide a very valuable source of information on how deaths are related to other factors.
| Area | Cardiovascular Disease | Other Causes | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Water Counties |
642 | 556 | 1198 |
| Soft Water Counties |
1255 | 216 | 1971 |
It was found that taking into account all possible causes for the differences in death that:
The hard water regions have the lower death rates.
The soft-water regions, which are the areas in the coastal plains, have the higher death rates.
Water Pollution and How it Occurs
Point Source Pollutants
Pollutants that enter into the system at one single point.
- Gas storage tanks -- Metal tanks set into the ground can sometimes rust and develop a leak.
- Sewage Treatment Plants -- Often discharge wastes into nearby water source after treatment.
- Laundromats and carwashes -- Detergents and chemicals dumped onto the round seep down to contaminate groundwater source.
- Industrial Plants -- often discharge waste products into nearby water source.
Non-Point Source Pollutants
- Fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides applied to fields, gardens, and lawns.
- Leaking sewers in a city.
- Storm sewers.
Flow of Pollutants
Ground water - flows along the gradient in the water table, taking a path that is perpendicular to the contours. Pollutants in the groundwater will flow in plumes along the same path. When a pollution source is introduced into the groundwater, the resulting plume will only affect areas downgradient from the source. Areas upgradient of the source, to the sides of the plume or below the plume will not be contaminated. Groundwater flows relatively slowly. On Long Island a typical rate of flow is about one foot per day near the water table. As the contaminant plume travels it becomes somewhat broader and more dilute as it slowly mixes with the surrounding cleaner water. Depending upon the original concentration of the plume and the distance the plume travels the contaminants may become so diluted that eventually the concentrations are lower than drinking water standards.
Selected Water Pollutants
- Oxygen Demanding Waste Biochemical Oxygen Demand -- When waste uses up oxygen needed for bacteria or other life.
- Pathogenic Organisms
- Fecal Coloform Bacteria -- found in fecal matter. Used to measure sewage presence in water.
- Not dangerous for the most part.
- Cryptosporidium -- Bacteria, can be lethal. Infested Milwakee water supply at one point.
- Giardin -- Found in deer and other animals. Why you shouldn't drink from wild streams without filtering water first.
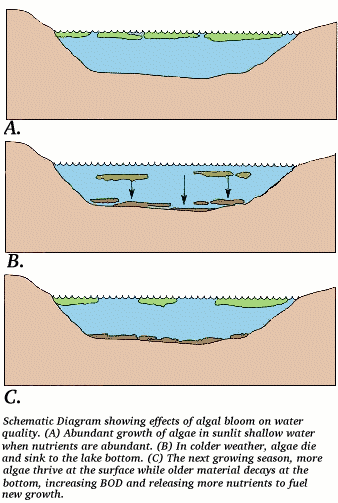
- Anoxia -- When the overabundance of nutrients causes an algal bloom in the spring and early summer. Later in the summer these algae settle to the bottom and bacteria feed on the algae which uses up the free oxygen in the bottom waters of the body of water.
- Hypoxia -- When the algeal bloom results in a low level of oxygen within the water body which will not sustain normal bottom dwellers or fish.
- The lack of oxygen causes the existing life within the water body to die, and decay. This, in turn, allows time for the replenishment of oxygen, as well as providing nutrients for later life.
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
Hazardous Chemicals (Toxic organic and Inorganic compounds).
- Many used to come from Dry Cleaners waste products.
Radioactive Chemicals
- Sediments -- In zones of high erosion, sediments can really clog up many streams and ponds.

